Checkpoints
Create a Firebase project
/ 25
Register your app
/ 25
Set up authentication and a database
/ 25
Add a customer page to your web app
/ 25
Build a Serverless Web App with Firebase
- GSP643
- Overview
- Objectives
- Task 1. Provisioning the Firebase environment
- Task 2. Install the Firebase CLI
- Task 3. Setup a Firestore Database
- Task 4. Create a Firebase project
- Task 5. Register your app
- Task 6. Authenticate to Firebase and Deploy
- Task 7. Set up authentication and a database
- Task 8. Scenario: set up the application
- Task 9. Configure Firestore authentication and add sign-in to your web app
- Task 10. Deploy your application
- Task 11. Add a customer page to your web app
- Task 12. Let users schedule appointments
- Task 13. See Firestore real-time updates
- Congratulations!
GSP643

Overview
Twelve years ago, Lily started the Pet Theory chain of veterinary clinics. The Pet Theory chain has expanded rapidly over the last few years. Their old appointment system is not able to handle the increased load or allow clients to schedule their own appointments, so Lily asked Patrick, in IT, and Ruby, a consultant, to build a cloud-based system that easily scale. In this lab you will build a fully fledged Firebase web app that allows users to log information and schedule appointments in real time.
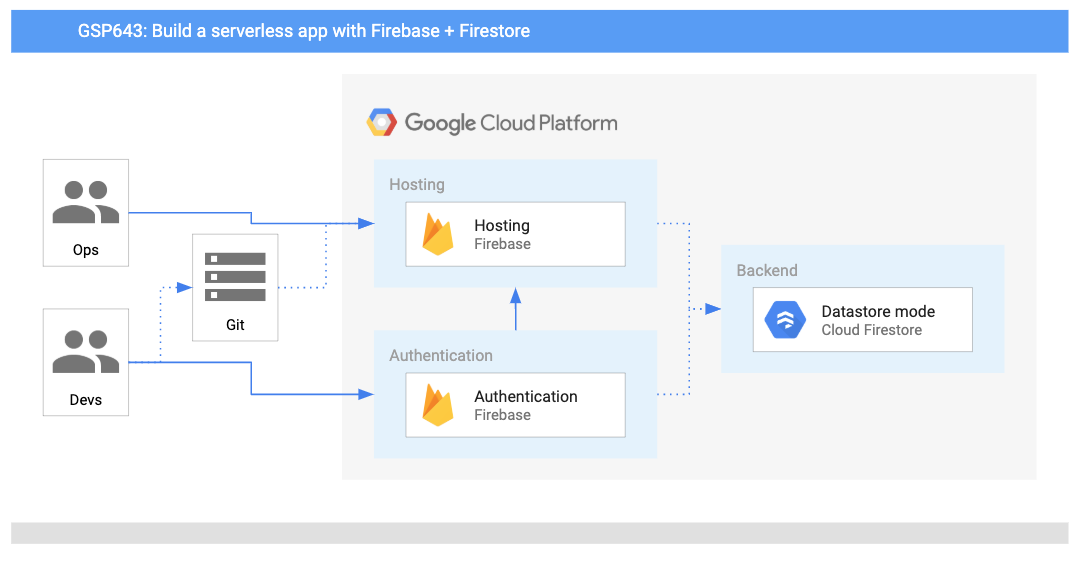
Architecture
This diagram gives you an overview of the services you will be using and how they connect to one another:
Objectives
In this lab, you will learn how to:
- Enable the Firebase API in your Google Cloud project.
- Create and configure a Firebase project.
- Configure Firestore Security to automate server-side authentication and authorization.
- Add Google sign-in to your web app.
- Configure your database so users can add their contact information.
- Explore and deploy code that allows users to schedule appointments.
- Explore Firebase's real time updates in your web app.
Prerequisites
This is a intermediate level lab. This assumes familiarity with the Cloud Console and shell environments. Experience with Firebase will be helpful, but it is not required. Before taking this lab it is recommended that you have completed the following lab:
You should also be comfortable editing files. You can use your favorite text editor (like nano, vi, etc.) or you can launch the code editor from Cloud Shell, which can be found in the top ribbon:
Once you're ready, scroll down and follow the steps below to setup your lab environment.
Task 1. Provisioning the Firebase environment
Ruby sends Patrick an email:
|
Ruby, Software Consultant |
Hi Patrick, Awesome work last week. Great to see that the clinic's data has been migrated to Firestore! It looks like the next task is to use Firebase to host the Pet Theory website. Ruby |
|
Patrick, IT Administrator |
Hi Ruby, I haven't heard of Firebase hosting before, what are the benefits? Where would I get started? Patrick |
|
Ruby, Software Consultant |
Hi Patrick The primary benefit of Firebase hosting is that it is serverless, so there is no infrastructure to manage. Security rules are also embedded within the application, so permissions can be restricted to minimize issues when handling customer data. It also has a "pay as you use" model, which means Firebase is a comprehensive mobile development platform for our use case. Ruby |
|
Patrick, IT Administrator |
Hi Ruby Sounds like Firebase will make security and infrastructure management (a big part of my job) a whole lot easier. I'm excited to not be billed for idle servers either! Patrick |
Ruby sends Patrick some background information in an email, and they hold a meeting to work out the key activities. From this meeting they determine that he needs to:
- Add the Firestore CLI to the Google Cloud project.
- Create a Firestore Database.
- Configure a Firebase project.
- Establish security policies.
Next, help Patrick accomplish these tasks.
Task 2. Install the Firebase CLI
-
Copy the IDE link from the Lab Details panel and paste it into a new browser tab to open Cloud Code.
-
Open a terminal to access the command line. In the left panel, click the Application menu (
) > Terminal > New terminal.
-
Clone the GitHub repository from the command line:
-
In the left panel, click the Explorer icon, and then Open Folder > pet-theory > lab02. Click OK.
-
Open a terminal
-
Install the necessary node packages:
Output:
You are now ready to create a Firestore database.
Task 3. Setup a Firestore Database
In the terminal prepare the environment to use a Firestore Database.
- Set your project region to
:
-
Enable
App Engineapplications:gcloud app create --region={{{project_0.startup_script.app_region|REGION}}} -
Create a Firestore database:
gcloud firestore databases create --region={{{project_0.startup_script.app_region|REGION}}}
You are now ready to create a Firestore project and link it to your Google Cloud account.
Task 4. Create a Firebase project
Open the Firebase console in an incognito window.
-
Click the account icon in the upper right-hand corner of the page and ensure that it is the Qwiklabs student account that you have been provisioned for this lab.
-
Then click Add project. When prompted for a project name, Use the Project ID from the drop-down menu.
-
Accept the Firebase terms and click Continue. Confirm the "Pay as you go" billing plan.
-
Click Continue and on the following page disable the Google Analytics for your Firebase Project.
-
Then click Add Firebase. Click Continue when you see a prompt that says your new project is ready:
Test completed task
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 5. Register your app
After completing the last step, you should be in the Firebase Console. If you close that page, you open another incognito tab and use the following link to the Firebase Console.
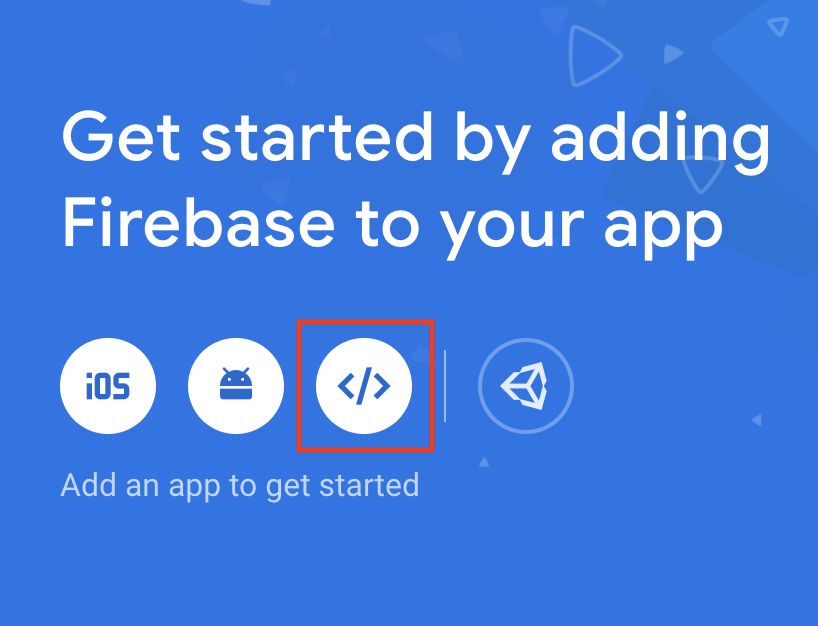
- Select the web icon (highlighted below) from the list of "Get started by adding Firebase to your app" icons:
-
When prompted for an "App nickname", type in Pet Theory.
-
Then check the box next to "Also set up Firebase hosting for this app".
-
Click on the Register app button.
-
Click Next > Next > Continue to console. You should now be on the following page:
You have now configured Firebase for the project. Next, you will initialize the project to reference your Firebase host.
Test completed task
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 6. Authenticate to Firebase and Deploy
Use the IDE to connect to Firebase and deploy your application. Type the commands in the terminal available in the editor.
- Authenticate to Firebase:
-
Enter in Y if asked if Firebase can collect error reporting information and press Enter.
-
Copy and paste the URL generated in a new incognito browser tab and press Enter (directly clicking on the link results in an error).
-
Select your labs account and then click Allow. Click on Yes, I just ran this command to proceed, then confirm your session ID by clicking Yes, this is my session ID. You will then be given an access code:
-
Copy the access code, paste it in the Cloud Shell prompt Enter authorization code:, and press Enter. You should receive output similar to the following response:
Output:
- Now initialize a new Firebase project in your current working directory:
Running this command will step you through setting up your project directory and Firebase products.
- You will be asked to select the Firebase CLI features you want set up in this folder. Use the arrow keys and the spacebar to select Firestore and Hosting. Ensure your shell matches the following and then hit Enter:
- Then run through the rest of the steps to configure Firebase:
- Key down to Use an existing project and press Enter.
- Select your Qwiklabs Project ID from the list (it's the one that starts with "qwiklabs-gcp-") then Enter.
- Press Enter and then N to keep your firestore.rules file.
- Press Enter and then Y to keep your firestore.indexes.json file.
- Press Enter to keep your public directory and then N to disallow rewrites to your /index.html file.
- Press Enter to Set up automatic builds and deploys with GitHub? and press N.
- Enter in N when prompted to overwrite your 404.html file.
- Enter in N when prompted to overwrite your index.html file.
You should receive the following output:
The local configuration is now complete. Now the database authentication step is required to provide access between the services.
Task 7. Set up authentication and a database
Return to the Firebase Console to complete this step.
-
Click on the Project Overview button in the left-hand navigation menu.
-
Select Authentication tile and then click on Get Started:
-
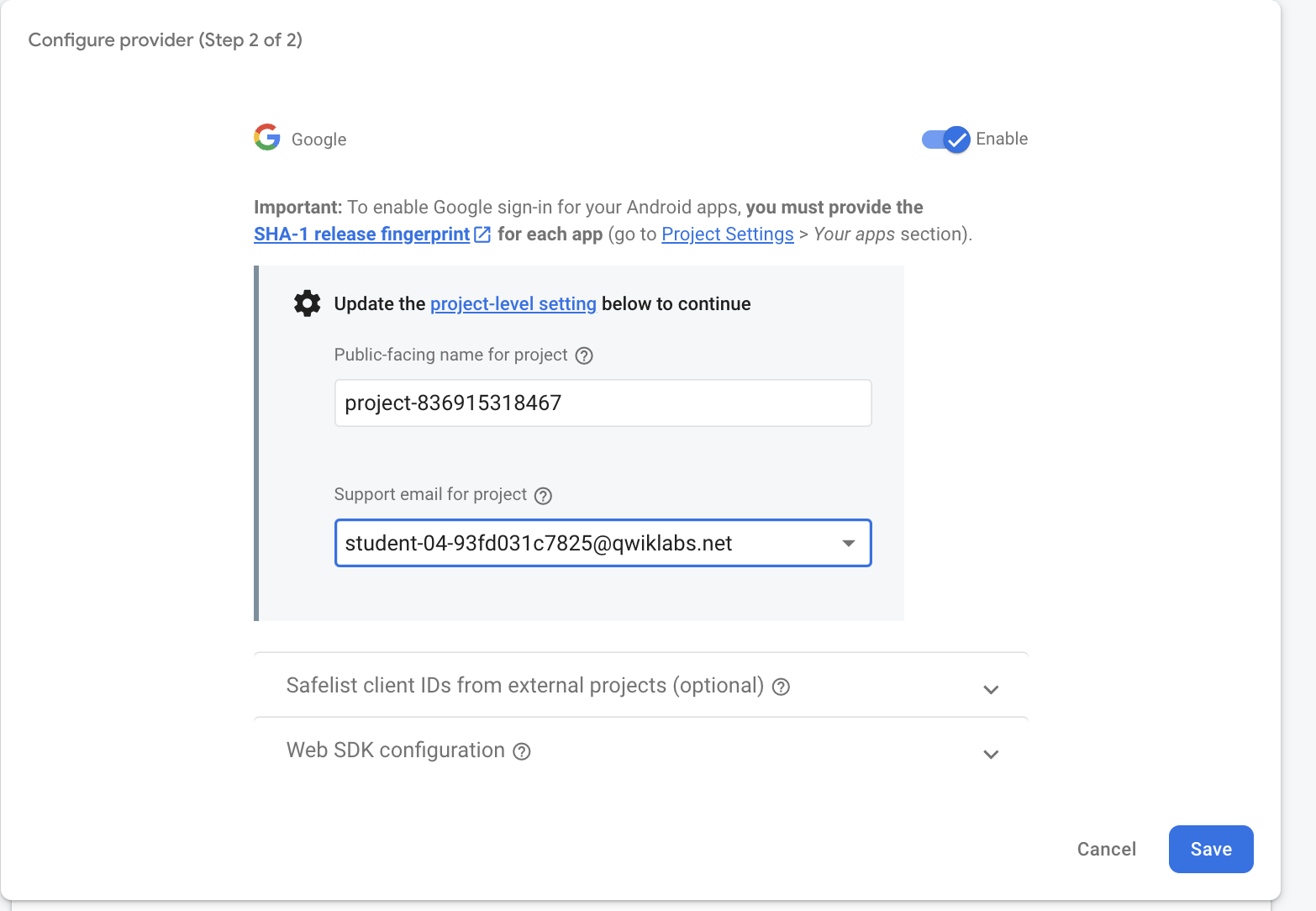
Click on Sign-in providers and then, click on the Google item.
-
Click the enable toggle in the top right corner and for the Support email for project select your lab account from the drop down list. Your page should now resemble the following:
- Once you have verified the above, click on the Save button.
You have now set up Firestore authentication. In the following step you will work on hosting the application with Firebase.
Test completed task
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 8. Scenario: set up the application
You have assisted Patrick in setting up a working Firebase hosting environment where a web developer can deploy their code. However, Patrick has never enabled Firebase authentication nor has he deployed code to Firebase, so he emails Ruby for some help...
|
Patrick, IT Administrator |
Hey Ruby, Thanks for all the tips! The Firebase environment looks like it is all set up. My next task is to deploy the website developers' code. Can you help me understand what this entails and what I need to do next? Patrick |
|
Ruby, Consultant |
Hi Patrick, That's great to hear! I'll send you the instructions on how to run the application and add the following features:
Ruby |
|
Patrick, DevOps Engineer |
Hi Ruby That sounds like it will be quite a bit of work. Does that mean I'll have to make structural changes every time I want to add something new? Not to mention the time it will take to see those updates... Patrick |
|
Ruby, Consultant |
Hey Patrick You can do most of the heavy lifting with Firebase libraries. Seeing your updates in your browser is as simple as calling Make changes, deploy, and see your changes on the website! Ruby |
|
Patrick, IT Administrator |
Hi Ruby Wow, that's very comforting! Firebase hosting just gets better and better :-) Patrick |
Now that Patrick has a better understanding of what is required, you will help him deploy Pet Theory as a Firebase application.
Task 9. Configure Firestore authentication and add sign-in to your web app
Return to the Terminal for this step. You should still have your command line session open from the previous Firebase initialization.
- Run the following command to list the folders and files in your
lab02directory:
- Make sure that your output resembles the following:
- Use the code editor to open the
pet-theory/lab02/firestore.rules:
Task 10. Deploy your application
With all the changes made, you are ready to deploy the application. Ensure you are still in the pet-theory/lab02 folder.
- Run the following command to deploy your firebase application:
Output:
- Copy the hosting URL (should resemble
[PROJECT-ID].web.app) and open it in a new tab. - Click on the Sign in with Google button:
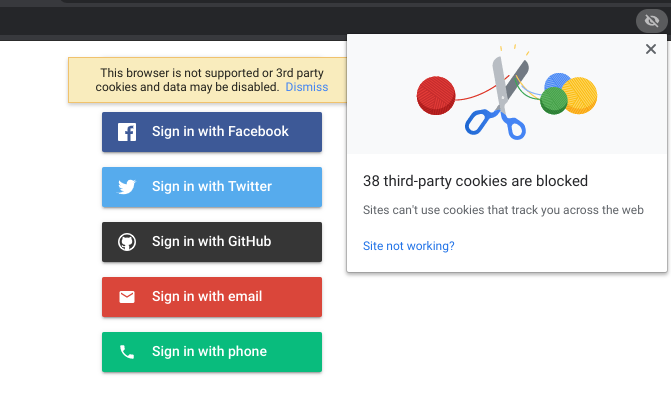 This can be done in Chrome by clicking the eye icon at the far right of the url tab and following the blue links in the popup. Click on the site not working? link to update your browser settings to accept cookies.
This can be done in Chrome by clicking the eye icon at the far right of the url tab and following the blue links in the popup. Click on the site not working? link to update your browser settings to accept cookies.
- Select your Google account. The following page opens:
You have now deployed code to let users use Google authentication to access the appointments app.
Task 11. Add a customer page to your web app
Return to the Terminal and use the editor to view the files in the public folder.
- Open the
customer.jsfile and copy and paste the following code:
- Open the
styles.cssfile and paste in the following code:
- From the command line run the following command:
Output:
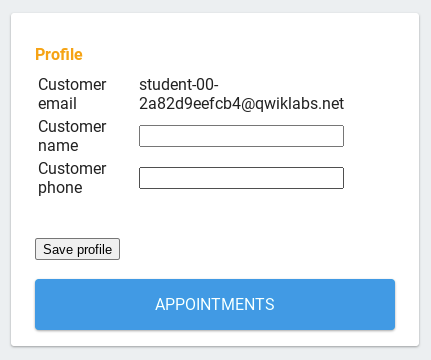
- Go to your application tab and hard refresh the page with CMND+SHIFT+R (Mac) or CTRL+SHIFT+R (Windows). Simple refreshing will not display the needed updates. Enter some customer info—make up a name and phone number and click Save profile.
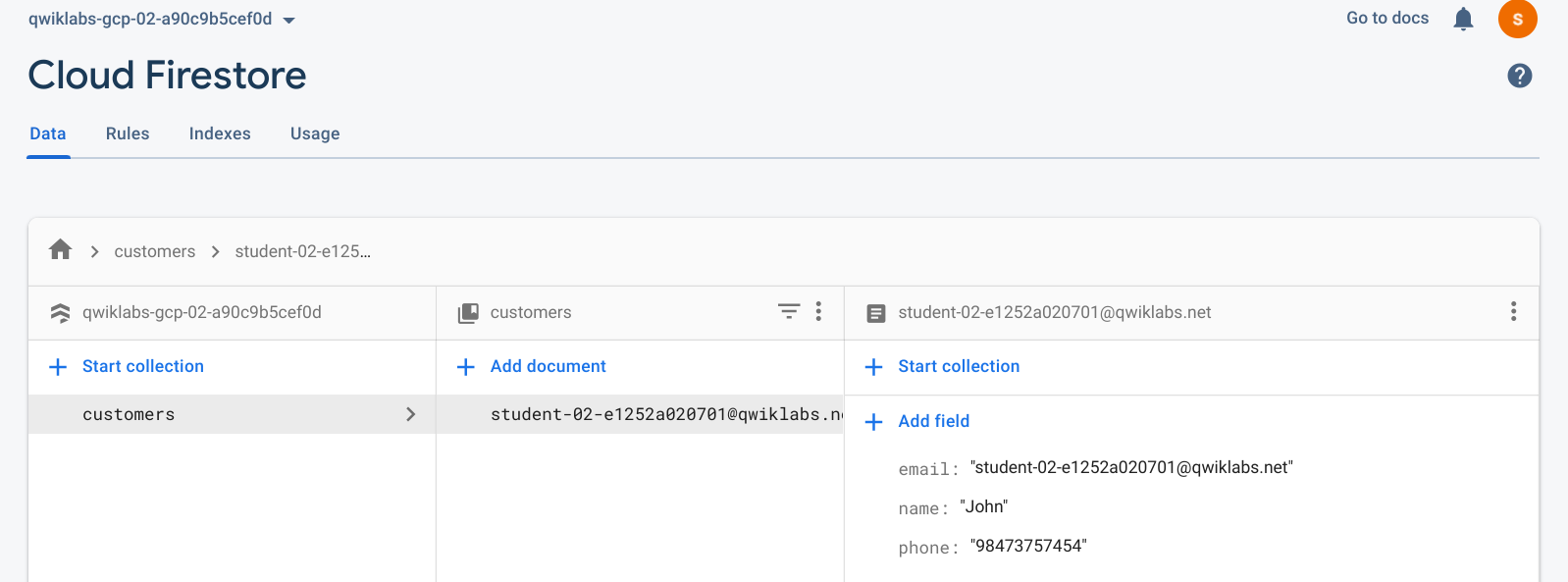
- Return to the Firebase Console and click Build > Firestore Database to view the profile information saved:
- Return to the web app page and click on the Appointments link. You will see a blank page since it has not deployed the appointments code yet.
Test completed task
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 12. Let users schedule appointments
Build out the page that allows users to schedule appointments.
-
Return to the Code Editor tab. You will add code to two files in the
publicdirectory. -
From the side menu, select appointments.html and paste in the following code:
- Now open the appointments.js file and paste in the following code:
- Now that your files have been built, view your changes. Run the following command in Cloud Shell to deploy your application:
Output:
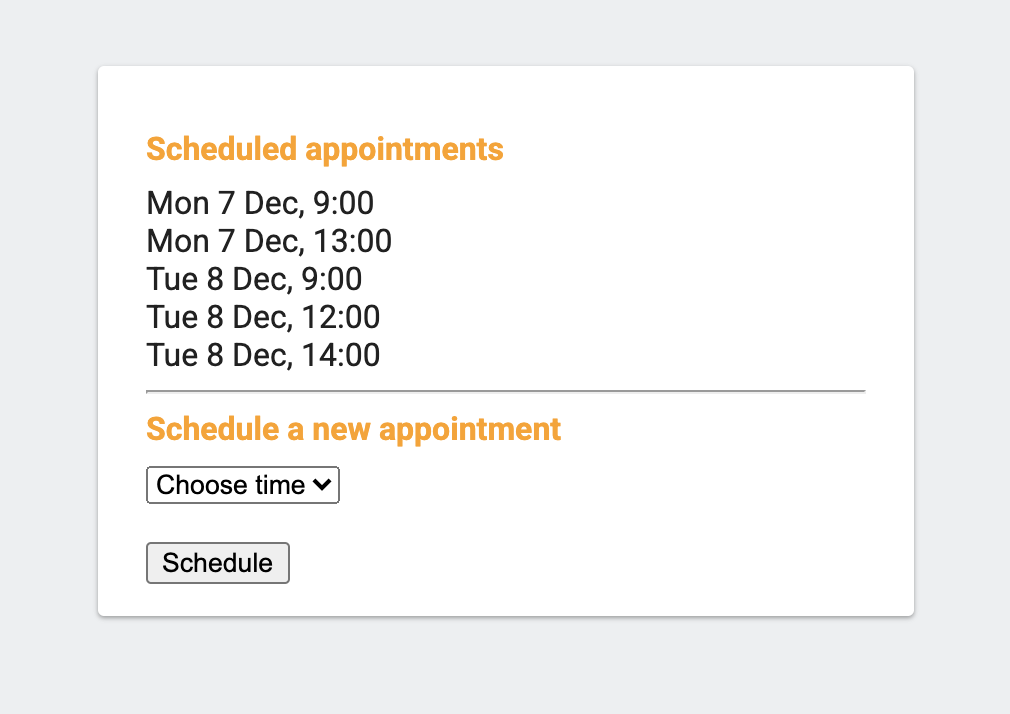
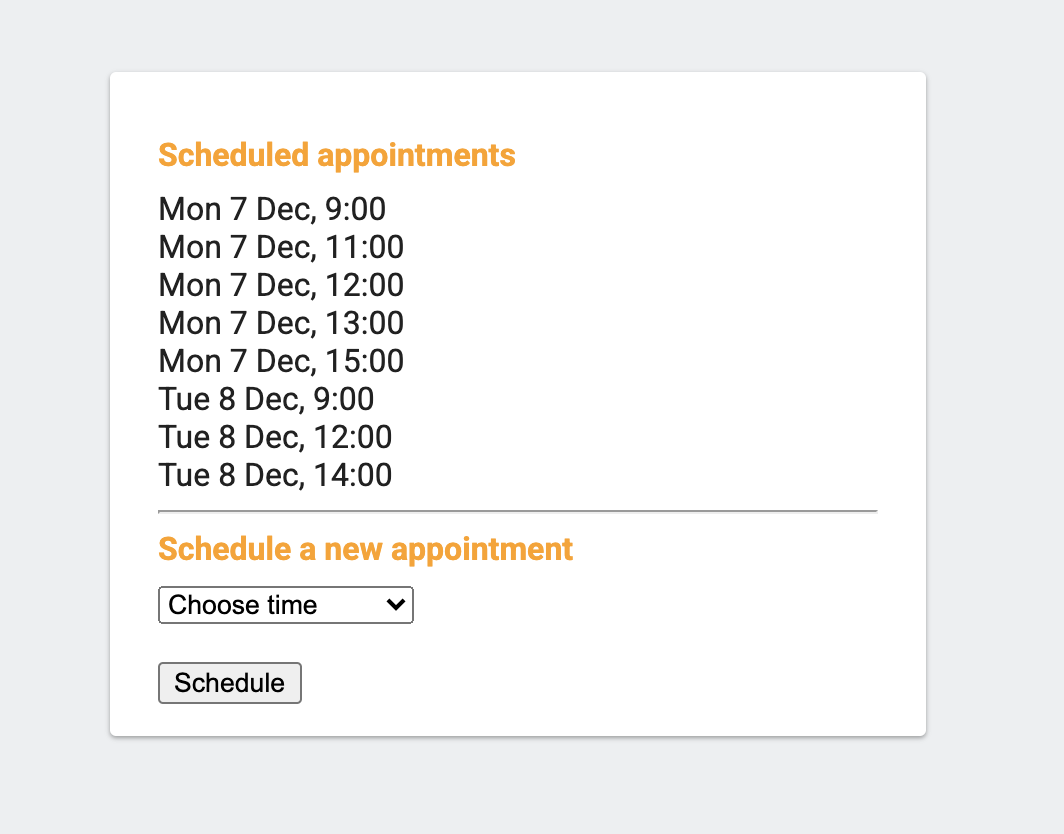
- Refresh your web app tab, where you previously got the blank page. Go ahead and schedule a couple of appointments:
-
Now go to the Firebase Console, click Build > Firestore Database and select the
appointmentscollection that you just created under your user. -
You should see a similar collection of appointments codes:
Task 13. See Firestore real-time updates
Firestore is a real-time database. Add real time updates to the application to take advantage of this.
-
Open a new browser tab and point it to [PROJECT ID].web.app, then log in using the Google button and click Appointments.
-
Arrange the two browser tabs side-by-side. In the first browser window, schedule a new appointment.
-
Now look at your other browser tab—you should see the appointment automatically added without having to refresh:
Pretty cool! Firestore updates clients (web apps and native mobile apps) in real time, without the user having to refresh or reload.
- Go to the Firebase Console, click the Data tab in Cloud Firestore, and edit the data. You can even delete the
appointmentscollection under your user record. Both browser windows keep updating in real time.
Congratulations!
Throughout the course of this lab, you created a robust serverless web application with Firebase. After creating and configuring a Firebase Project, you added Firestore security to automate server-side authentication and authorization. You then went ahead and added Google Sign-in to your web app and configured your database so users can add contact info and appointments. Finally, you explored and deployed code that allows users to schedule appointments and saw Firebase's real time updates in your web app. You are ready to take more labs in this learning path.
Next steps / learn more
- Google Cloud - What is Serverless?
Google Cloud training and certification
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated January 30, 2024
Lab Last Tested January 8, 2023
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.